THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA

PRESIDENT’S OFFICE, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
NJOMBE REGION
FORM SIX PRE-MOCK EXAMINATION
CODE: 131/2 PHYSICS 2
(For Both School and Private candidates)
Time: 3:00Hours Wednesday 23th August 2023 (AM)
![]()
Instructions
1. This paper consists of six (6) questions.
2. Answer five (5) questions only
3. Each questions carries twenty marks.
4. Cellular phones and other unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
5. Non programmable calculators and NECTA mathematical tables may be used.
6. Write your examination number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
7. All writings must be in blue or black ink except for drawings which must be in pencil.
8. The following information may be used.
• Acceleration due to gravity g=9.8m/s2
• Permittivity of a free space=8.854x10¹²Nm-²kg-²
• Density of air p=1.29kg/m³
• Speed of sound, c=340m/s
• Y for Copper is 12x10¹⁰N/m²
• Y for steel is 20 x 10¹⁰N/m²
• Plank's constant=6.63x10-³⁴Js
• Mass of proton and neutron are 1.007825amu and 1.008665amu respectively.
- a. i) Differentiate between laminar flow from turbulent flow.
ii) State the continuity equation for the incompressible fluid flowing through the pipe.
iii) The flow rate of water from a tap of diameter 1.25cm is 3litres per minute. The coefficient of viscosity of water is 10-3 Pa-s. Characterize the flow.
b. i) How will you compare the viscosity of two liquids.
ii) At what speed will the velocity head of a stream of water be equal to 40cm.?
iii) The reading of a pressure meter attached to a closed pipe is 2.5 x 10⁵Nm-². On opening the valve of the pipe, the reading of the pressure meter reduces to 2.0 x 10⁵Nm-². Calculate the speed of water flowing through the pipe.
c. A large tank contains water to a depth of 10m.Water emerges from a small hole on the side of the tank 20cm below the level of the water surface. Calculate:
i) The speed at which water emerges from the hole.
ii) The distance from the base of the tank at which water strikes the floor on which the tank is flowing.
02. a. i) How does stationary wave differ from progressive wave. Give two points.
ii) State the principle of superposition as applied in wave motion.
iii) The fundamental frequency of the sonometer wire increases by 5Hz if its tension is increased by 21%. How will the frequency be affected if its length is increased by 10%.
b. i) Why changes in pressure do not affect the velocity of sound?
ii) At what temperature will the velocity of sound in air be twice than the velocity in air at 0°C.
c. i) Why are bells made up of metal not of wood.
ii) What is meant by Doppler effect.
iii)A cyclist and a railway train are approaching each other. The cyclist is moving at 10m/s and the train at 20m/s. The engine drives sound a warning siren at frequency of 480Hz.Calculate the frequency of the note heard by the cyclist before and after the train has passed by. (Speed of sound in air=340m/s).
3. a. i) What is meant by poisson's ratio and elastic fatigue as it is used in properties of matter.
ii) Why do spring balances show wrong readings after they have been used for a long time.?
iii) Two exactly similar wires of steel and copper are stretched by equal forces, if the total elongation is 1cm.Find how much each wire is elongated.
b. Briefly explain the classification of materials based on their elastic properties.
c. i) What is meant by the term surface tension.
ii) A spherical drop of mercury of radius 2mm falls to the ground and breaks into 10 small drops of equal size. Calculate the amount of work to be done in the process. Surface tension of mercury is 4.72x10-¹N/m.
4. a i) Distinguish electric field and electric dipole.
ii) Four-point charges of -4uC, +2uC, -2uC and +4uC are placed on corners ABCD of square respectively.
Determine the strength of the electric field at the centre of a square of side 2m.
b. i) What is meant by the term electric potential
ii) Two positive point charges of 16 x 10-¹⁰C and 12x10-¹⁰C are placed 10cm apart. Find the workdone in bringing the two charges 4cm closer
c. i) Two spheres of different capacitance are charged to different potentials. They are then joined by a wire. Will a total energy increase, decrease or remain the same?
ii) Calculate electric potential at the surface of the silver nucleus having radius3.4x10-¹⁴m given that the atomic number of silver and charge e on proton are 47 and 1.6 x 10-¹⁹C respectively.
5. a. i) Distinguish between magnetic field and magnetic flux.
ii) A copper wire has 1.0x 10²⁹ free electrons per cubic metre, a cross section area of 2mm² and carries a current of 5A. The wire is placed at right angle to a uniform magnetic field of strength 0. 15T.Calculate the force acting on each electron.
b. i) State Biort sarvat law and describe each term in the law.
ii) A solenoid has a length of 1.23m and inner diameter 4cm it has 5 layers if windings of 850 turns each and carries a current of 5.57A, what is the magnitude of the magnetic field at the centre of the solenoid.
(c). With the aid of a well labelled diagram describe the principle, construction and mode of action of a moving coil galvanometer.
6. a. i/ What are the main two experimental observation of photoelectric effect that are against classical physics. (2marks)
ii/ Monochromatic light of wavelength 4500A° is incident on sodium surface of work function 2.3eV. Determine the energy of incident photons, maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons and stopping potential of sodium. (6 marks)
b. i) Explain how stability of an atom is related to its binding energy. (2 marks)
ii) Obtain binding energy of the nuclei 26Fe56 and 83Bi209 in units of MeV from the following data. m(26Fe56) = 55.934939u m(83Bi209) = 208.980388u.
Which nucleus has greater stability than the other? (5 marks)
c. A nuclear reactor is a device in which controlled chain reaction takes place to produce heat for electricity generation. Describe the essential parts of a nuclear reactor. (5 marks)
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 86
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 86
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA

PRESIDENT’S OFFICE, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
NJOMBE REGION
FORM SIX PRE-MOCK EXAMINATION
CODE: 131/1 PHYSICS 1
(For both school and private candidates)
TIME: 3:00 HRS Thursday, 17th August 2023 P.M
![]()
Instructions
1. This paper consists of section A and B with a total of ten (10) questions.
2. Answer all questions in section A and choose two (2) questions from section B.
3. Marks for each equation or part thereof are indicated.
4. Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
5. All writing must be in blue or black ink except drawing which must be in pencil.
6. Cellular phones and any unauthorised materials are not allowed in the examination room.
7. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
8. Where necessary the following constant(s) may be used
i. Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10ms−2
ii. Density of water=103kgm−3
iii. Speed of sound in air, v=340m/s
iv. Atmospheric pressure=1.013x105N/m2
v. Pie,
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 85
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 85
OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM SIX MOCK EXAMINATION – 2022
PHYSICS. - 3A
Code 131/1
Time: 3 Hours
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of three (3) questions.
- Answer all question
- Question number one (1) carries 20 marks and other two (2) carries 15 marks each
- Calculations should be shown clearly
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
- The following information may be useful:
-
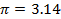
- Specific heat capacity of water Cw = 4200JKg-1K-1
- Specific heat capacity of copper Cc = 400JKg-1K-1
- You are provided with a retort stand, pendulum bob a thread a stop watch and a metere rule.
Proceed as follows:
- Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure below, where L is the distance from the point of attachment of the bob to the point of suspension of a thread on a retort stand
- Starting with L=100cm displace a bob through a small angle sideways and then release it so that it can oscillate to and fro. Record the time t in seconds for 20 oscillations and the periodic time T
- Repeat the procedure in 1(b) above for values of L= 80cm, 60cm, 40cm and 20cm
- Tabulate your results
- Plot a graph of L(cm) against T2(S2)
- Compute for values of g from the relation g T2 = 4π2 (L + x)
- Read and record the value of L – axis intercept
- What does the value of L – axis intercept on the graph represent
- What is the aim of performing this experiment
- The aim of this experiment is to determine the emissivity of aluminium at 65°C
Proceed as follows:
(a)Heat some water in a beaker while the water is heated do the following
- Using the rubber band available lightly cover the external area (side and bottom) of the calorimeter with the piece of aluminium foil provided
- Weigh the calorimeter together with its aluminium foil cover and record its mass m in kg
- Measure the average external diameter d of the calorimeter and its height using a vernier caliper, hence determine its external area A using the equation
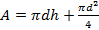
- Note and record the room temperature
- Open the jaws at the clamp on the retort stand and adjust it so that the calorimeter can rest on it steadily. You may have to twist the clamps little so that the base of the calorimeter can sit on securely
(b)Pour a hot water at least 85°C into the calorimeter so that it just above fill the calorimeter, put the wooden cover on the calorimeter lightly do not tighten otherwise it will not come off easily. Put the thermometer into the calorimeter and close the hole in the wooden cover using some cotton wool. Rest the calorimeter on the clamps
(c) Starting with the temperature ![]() of the water at about 75°C and taking the reading for every 2 minutes, record the temperature
of the water at about 75°C and taking the reading for every 2 minutes, record the temperature ![]() corresponding to the time t of cooling until the temperature drops up 55°C and while doing this fan the calorimeter with some sheets or paper or air continuously so that the current of air cools the calorimeter record the value of
corresponding to the time t of cooling until the temperature drops up 55°C and while doing this fan the calorimeter with some sheets or paper or air continuously so that the current of air cools the calorimeter record the value of ![]() and t
and t
(d) Remove the wooden cover from the calorimeter and weight the calorimeter with water note and record the mass M in kg
(e)
- Plot a graph
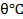 agaisnt time (min) and from it determine the slop
agaisnt time (min) and from it determine the slop 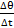 at the temperature of 65°C
at the temperature of 65°C - Calculate the rate of heat loss to the surrounding
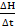 given that
given that 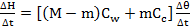
- Using Newton’s law of cooling determine the value of K in the following equation
![]()
- What is the physical meaning of K
- Calculate the value of the ratio
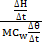
- What is the physical meaning of the ratio in (v) above?
- The aim of the experiment is to determine the resistivity of the material of wire W and the unknown resistance R.
Proceed as follows
- Connect the circuit as shown in the figure below in which the unknown resistence R and the wire W connected in series are placed in the right and gap of the metre bridge while the standard resistance
RS= 4Ω placed in the left hand gap
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 63
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 63
OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM SIX MOCK EXAMINATION – 2022
PHYSICS. - 2
Code 131/2
Time: 3Hours
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of six (6) questions.
- Answer any five (5) questions
- Each question carries 20 marks.
- Marks for each questions are indicated
- Mathematical tables and non- programmable calculators may be used.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
- The following information may be useful:
- Acceleration due to gravity g= 9.8m/s2
- Density of Ice = 1g/cm3
- Young’s modulus of steel = 2 x 1011N/m2
- Young’s modulus of brass = 1 x 1011N/m2
- Permittivity of free space,
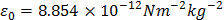
- Permeability
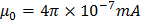
- Speed of light, C=3 x 108 ms-1
- Planck’s constant, h= 6.63 x 10-34Js
- Speed of sound in air, V=340m/s
- Charge of an electron, e=1.6 x 10-19C
- Mass of electron, Me,=9.1 x 10-31kg
- Coefficient of water = 1.0 x 10-3Pas
- 1. a.m.u = 931.5 Mev
- Pie,
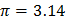
- (a)give briefly explanation of the following as applied in fluid dynamics
- Compressible fluid
- Non viscous fluid
- Turbulent flow
(b)
- Stoke’s law for the viscous force F acting on a sphere of radius “a” falling with velocity V through a large expense of fluid of coefficient of viscosity Ϩ is expressed by the equation F = 6πaϨV, state why this equation is true only for sufficiently low velocities
- A drum of 30cm radius has a capacity of 2.2 x 105cm3. It contains 1.98 x 105cm3 of water and is placed on a solid block of exactly the same size of the drum. If small hole is made at lower end of drum perpendicular to its length, find the horizontal range of water on the ground in the begging. State two main assumptions made during your calculations
(c)
- Write down Poiseulle’s formula and state two conditions in which it is based
- A horizontal tube of diameter 2mm and length 50cm is connected at the bottom of a cubical tank whose area is 0.5m2. At what time will the tank be one quarter full if the tank is initially full of water
(d) Explain the following observations
- Machine parts are jammed in water
- Two ships are moving parallel and close to each other, they experience an attractive force.
- The parachute used while jumping from airplane?
- (a)(i)Explain the conditions necessary for the formation of stationary waves in air
(ii)What are the factors which determine the period of free oscillations of a mechanical system?
(b)A 60cm long wire is in unison with a turning fork of frequency 512HZ when stretched by a load of density 10g/cm3 hanging vertically. The load is then immersed in water. By what percent the length of the wire should be reduced to bring it again in unison with the same turning fork?
(c)(i)A red is observed in the light received on earth from galaxies. Explain what is a red shift and how it occurs
(ii)In the measurement of blood flow in a patient of CORONA VIRUS, ultrasound of frequency of 10.0MHZ is incident at an angle of 30° to the blood vessel and a Doppler shift in frequency of 8.8 KHZ is observed. If the velocity of ultrasound can be taken as 2.2Kms-1 and the diameter of blood vessel is 0.8cm. Calculate the blood flow velocity and volume flow velocity flow rate of blood
(d)A parallel beam of sodium light is incident normally on a diffraction granting. The angle between the two first order spectra on either side of the normal is 27°42'. Assuming that the wavelength of a light is 5.893 x 10-7 m. Find
- The number of rulings per mm on the grating
- The greatest number of bright images obtained
- . (a) Elastic moduli elastic limit and strengths of material are all quoted with the same unit, Pascal’s. Explain the differences between these three physical quantities
(b) Explain the following observation
- Stresses and strains rather than forces and extensions are generally considered when describing the elastic behavior of solid
- A rubber band have a smaller force constant than that of an iron wire
(c) A 3.0m length of a rod is suspended horizontally from the ceiling using two vertical wires of equal length tied to its ends. One of the wires is made of steel of across sectional area 1 x 10-3m2 and the other is made of brass of cross sectional area 4 x 10-3m2. Find the position along the rod at which a weight may be hung to produce
- Equal stresses in the wires
- Equal strains in the wires
(d)(i)Define mean free path of a molecules of a gas and state how it is affected by temperature.
(ii) If the mean free path of molecules of air at ![]() and 1 atmospheric pressure is
and 1 atmospheric pressure is
2 x 10-7m. What will the mean free path be at 1 atmospheric pressure and 27![]() ?
?
- (a)(i)What similarities do electrostatic forces have to gravitational forces? Give four (4) points.
(ii) Give three (3) properties of an equipotential surface
(b)(i) Define equipotential
(ii)Three charges of 2μC, - 3μC and 4μC are placed on the three corners A, B and C of an equilateral triangle of sides 2m respectively. Determine the electric potential at a point half way between AB
(c)Explain the effect of doubling the separation of the plates of a parallel – plate capacitor on the energy stored by the capacitor
- When the capacitor is isolated
- When the capacitor is connected to battery
- In each case above account for the energy changes which accur
(d)An uncharged capacitor of capacitance C1= 8μF is connected to a power supply and charged to a potential difference V= 120V. The power supply is disconnected. If another uncharged capacitor of capacitance C2=4μF is connected to the capacitor C1, determine
- The final potential difference across each capacitor
- The final charge on each capacitor
- The initial and final energy of the system
- Account for the energy difference
- (a)(i)Distinguish between magnetic permeability from magnetic susceptibility regarding magnetic properties of materials
(ii)Use curie’s’ law to show magnetization for a paramagnetic material relates with absolute temperature
(b)(i)State Biot – savart law
(ii)Using Biot – Savart law, show that the magnetic field B formed at the centre of a narrow circular coil of radius R with N turns carrying a constant current and placed in air is given by ![]()
(c)A coil is tightly wound around an iron cylinder having 2400 turns per metre, calculate
- The magnetic field strength due to magnetization current of magnitude 0.22A
- The magnetic susceptibility if the magnetic field in the iron is 1.5T
(d)A coil with an inductance of 20H and resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with a battery of EMF 12V and a switch. What is?
- The rate of change of current immediately after the switch is closed
- The final current
- The current after 3.0S?
- How long after the switch is closed will the current be 0.40A?
- State four (4) basic Bohr’s postulates regarding to the hydrogen atom
- What is the meaning of negative energy of orbiting electron?
- The hydrogen atom is stable in the ground state. Why?
- The ionization energy of hydrogen is 13.6eV. What does it means?
- What is meant by half life of a radioactive element
- Draw a labelled sketch of the relation N=Noe-t to illustrate your answer
- The mass defect in the nuclear fusion reaction is 0.3%. What amount of energy will be in 1kg fusion reaction
- Sodium has a work function of 2.3 eV. Calculate
- Its threshold frequency
- The maximum velocity of the photoelectrons produced when the sodium is illuminated by light of wavelength 5 x 10-7m.
- The stopping potential with light of wavelength of 5 x 10-7m.
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 62
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 62
OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM SIX MOCK EXAMINATIONS – 2023
PHYSICS 1
Code 131/1
Time: 3Hours
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of section A and B with a total of ten (10) questions.
- Answer all question in section A and two (2) questions from section B
- Section A carries Seventy (70) marks in section B thirty (30) marks.
- Mathematical tables and Non-programmable calculator may be used.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
- The following information may be useful:
- Acceleration due to gravity g= 9.8m/s2
- Density of Ice = 1g/cm3
- Thermal conductivity of ice = 0.005 Cals-1 °C-1
- Latent heat of ice = 80 cal g-1
- Ratio of specific heat capacities Y=1.4
- Density of air = 1.3kg/m3
- Pie,
SECTION A (70 Marks)
Answer all questions from this section.
- (a)(i)Dimension can be treated as an algebraic quantity explain the meaning of this statement.
(ii)Write the dimension of a/b in the relation
![]() , where F is a force, x= distance and t is time
, where F is a force, x= distance and t is time
(b)What do you understand by the following terms?
- Absolute error
- Mean absolute error
(c) An experiment to determine the mass per unit area of an annular ring obtain the following readings.
Mass = ![]()
Internal diameter of the ring d1=(9.4 ![]() 0.1)mm;
0.1)mm;
External diameter the ring d2=(10![]() 0.1)mm
0.1)mm
The mass per unit area of annular ring is given by using the formula:
![]() Calculate the numerical value of Q
Calculate the numerical value of Q
- (a)(i) Is the motion of a simple pendulum strictly simple harmonic?
(ii)What is the relation between uniform circular motion and S.H.M?
(b)A cubical body (side 0.1m and mass 0.002kg) floats in water. It is pressed and then released so that it oscillates vertically. Find the time period.
- (a)(i)Where do we apply the concept of impulse?
(ii)A body of mass 10kg falls vertically on a muddy ground with a velocity of 20ms-1 and penetrates through a vertical depth of 0.3m. Calculate the average force exerted by the muddy ground
(b)(i)In a circular orbit, an earth satellite has the same P.E and K.E, everywhere in the orbit. Why?
(ii)A particle is projected vertically upward from the surface of the earth (Radius R) with a kinetic energy equally to half of the minimum value needed for it to escape. Calculate the height through which it rises above the surface of earth
- (a)(i) Is there any point on path of projectile where velocity and acceleration of projectile are perpendicular? Explain
(ii)Explain at what extent does the projectile motion change to free fall motion
(b)A hunter is intending to kill a lion which is at a distance of 40.2m from him by throwing his poisoned arrow to it. The arrow leaves the bow with the velocity of 20m/s at an angle of 60° to the vertical
- Explain with mathematical support if he is going to kill the lion
- If the hunter will not kill the lion, suggest the way in which the hunter can take if the horizontal distance and velocity of projection will remain constant.
- (a)(i)Why do two layers of cloth of equal thickness provide warmer covering than a single layer of cloth of double the thickness?
(ii) A body cools in 7 minutes from 60°C to 40°C. What will be its temperature after the next 7 minutes? The temperature of the surroundings is 10°C. Assume that Newton’s law of cooling holds good throughout process
(b)(i)Why Quilts are filled with fluffy cotton
(ii)A layer of ice 10cm thick is formed on a pond. The temperature of air is -10°C. Calculate how long it will take for the thickness of increase by 1 mm
- (a)What happens to the energy added to an ideal gas when it is heated
- At constant volume and
- At constant pressure
(b)(i)Give two ways in which the internal energy of the system can be changed
(ii)A quantity of air at 27°C is compressed slowly and then suddenly to one third of its volume. Find the change in temperature in each case
(c)(i)State Stefan’s law
(ii)A piece of metal loses 255J of heat per second by radiation when its temperature is 1200K and the temperature of the surrounding is 300K. What will be the rate of loss of heat when the temperature of the metal is 600K?
- (a)(i)Explain the meaning nuclear waste and the methods of disposal
(ii)How does the moon its position and movement affects tides on earth?
(b)With three main reasons comment the statement that excessive wind threats to plant growth.
SECTION B (30 MARKS)
Answer two (2) questions from this section
- (a)(i)State principle of potentiometer
(ii)The total length of potentiometer wire is 10m. The distance between the null points on the potentiometer wire for two cells is 60cm. If the difference between the e.m.fs of the cells be 0.4V, calculate the potential gradient along the wire and p.d between the ends of this wire
(b)(i)The drift velocity of free electrons is very small. Why does room light turn on at once as the switch is closed?
(ii)When a potential difference of 1.5V is applied across a wire of length 0.2m and area of cross – section 0.30mm2, a current of 2.4A flows through the wire. If the number density of free electrons in the wire is 8.4 x 1028m-3. Calculate the average relaxation time
(c)(i) Two batteries E1 and E2 having e.m.fs of 6V and 2V respectively and internal resistances of 2Ω and 3Ω respectively are connected in parallel across a 5Ω resistor. Calculate current through each battery and terminal voltage. (Hint: Apply Kirchhoff’s is laws)
(ii) Calculate the frequency at which the inductive reactance of 0.7H inductor is 220Ω
- (a)
- Why are holes carries present in n-type semiconductor?
- A transistor has low input impedance and high output impendence. Why?
- Why is silicon preferred to germanium in manufacturing semiconductor devices
(b)Study the circuit below of npn transistor
An npn transistor circuit above has ![]() = 0.985 and VBE = 0.3V. If VCC = 16V. Calculate R1 and Rc to place Q point at Ic = 2mA, VCE = 6V
= 0.985 and VBE = 0.3V. If VCC = 16V. Calculate R1 and Rc to place Q point at Ic = 2mA, VCE = 6V
- (a)
- Derive an expression for the output of an operation amplifier as differentiator
- In an integration the feedback capacitor has a capacitance of 0.01μF and a resistor of 10KΩ is connected to an input source of V1 = -1V. If the opamp is biased by + 10V determine the output voltage at time t= 0.5ms and the time taken for the opamp to saturate.
(b) (i) Why NAND and NOR gates are called Universal gates?
(ii)Obtain the truth table for the circuit shown below.
(c)An alarm system is controlled by three sensors, A, B and C. The system sounds it alarm when sensor A and B are on or when sensors B and C are on. Draw the truth table for the system and design its logic gate/
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 61
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 61
OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM SIX MOCK EXAMINATIONS – 2023
PHYSICS 1
Code 131/1
Time: 3Hours
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of section A and B with a total of ten (10) questions.
- Answer all question in section A and two (2) questions from section B
- Section A carries Seventy (70) marks in section B thirty (30) marks.
- Mathematical tables and Non-programmable calculator may be used.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
- The following information may be useful:
- Acceleration due to gravity g= 9.8m/s2
- Density of Ice = 1g/cm3
- Thermal conductivity of ice = 0.005 Cals-1 °C-1
- Latent heat of ice = 80 cal g-1
- Ratio of specific heat capacities Y=1.4
- Density of air = 1.3kg/m3
- Pie,
SECTION A (70 Marks)
Answer all questions from this section.
- (a)(i)Dimension can be treated as an algebraic quantity explain the meaning of this statement.
(ii)Write the dimension of a/b in the relation
![]() , where F is a force, x= distance and t is time
, where F is a force, x= distance and t is time
(b)What do you understand by the following terms?
- Absolute error
- Mean absolute error
(c) An experiment to determine the mass per unit area of an annular ring obtain the following readings.
Mass = ![]()
Internal diameter of the ring d1=(9.4 ![]() 0.1)mm;
0.1)mm;
External diameter the ring d2=(10![]() 0.1)mm
0.1)mm
The mass per unit area of annular ring is given by using the formula:
![]() Calculate the numerical value of Q
Calculate the numerical value of Q
- (a)(i) Is the motion of a simple pendulum strictly simple harmonic?
(ii)What is the relation between uniform circular motion and S.H.M?
(b)A cubical body (side 0.1m and mass 0.002kg) floats in water. It is pressed and then released so that it oscillates vertically. Find the time period.
- (a)(i)Where do we apply the concept of impulse?
(ii)A body of mass 10kg falls vertically on a muddy ground with a velocity of 20ms-1 and penetrates through a vertical depth of 0.3m. Calculate the average force exerted by the muddy ground
(b)(i)In a circular orbit, an earth satellite has the same P.E and K.E, everywhere in the orbit. Why?
(ii)A particle is projected vertically upward from the surface of the earth (Radius R) with a kinetic energy equally to half of the minimum value needed for it to escape. Calculate the height through which it rises above the surface of earth
- (a)(i) Is there any point on path of projectile where velocity and acceleration of projectile are perpendicular? Explain
(ii)Explain at what extent does the projectile motion change to free fall motion
(b)A hunter is intending to kill a lion which is at a distance of 40.2m from him by throwing his poisoned arrow to it. The arrow leaves the bow with the velocity of 20m/s at an angle of 60° to the vertical
- Explain with mathematical support if he is going to kill the lion
- If the hunter will not kill the lion, suggest the way in which the hunter can take if the horizontal distance and velocity of projection will remain constant.
- (a)(i)Why do two layers of cloth of equal thickness provide warmer covering than a single layer of cloth of double the thickness?
(ii) A body cools in 7 minutes from 60°C to 40°C. What will be its temperature after the next 7 minutes? The temperature of the surroundings is 10°C. Assume that Newton’s law of cooling holds good throughout process
(b)(i)Why Quilts are filled with fluffy cotton
(ii)A layer of ice 10cm thick is formed on a pond. The temperature of air is -10°C. Calculate how long it will take for the thickness of increase by 1 mm
- (a)What happens to the energy added to an ideal gas when it is heated
- At constant volume and
- At constant pressure
(b)(i)Give two ways in which the internal energy of the system can be changed
(ii)A quantity of air at 27°C is compressed slowly and then suddenly to one third of its volume. Find the change in temperature in each case
(c)(i)State Stefan’s law
(ii)A piece of metal loses 255J of heat per second by radiation when its temperature is 1200K and the temperature of the surrounding is 300K. What will be the rate of loss of heat when the temperature of the metal is 600K?
- (a)(i)Explain the meaning nuclear waste and the methods of disposal
(ii)How does the moon its position and movement affects tides on earth?
(b)With three main reasons comment the statement that excessive wind threats to plant growth.
SECTION B (30 MARKS)
Answer two (2) questions from this section
- (a)(i)State principle of potentiometer
(ii)The total length of potentiometer wire is 10m. The distance between the null points on the potentiometer wire for two cells is 60cm. If the difference between the e.m.fs of the cells be 0.4V, calculate the potential gradient along the wire and p.d between the ends of this wire
(b)(i)The drift velocity of free electrons is very small. Why does room light turn on at once as the switch is closed?
(ii)When a potential difference of 1.5V is applied across a wire of length 0.2m and area of cross – section 0.30mm2, a current of 2.4A flows through the wire. If the number density of free electrons in the wire is 8.4 x 1028m-3. Calculate the average relaxation time
(c)(i) Two batteries E1 and E2 having e.m.fs of 6V and 2V respectively and internal resistances of 2Ω and 3Ω respectively are connected in parallel across a 5Ω resistor. Calculate current through each battery and terminal voltage. (Hint: Apply Kirchhoff’s is laws)
(ii) Calculate the frequency at which the inductive reactance of 0.7H inductor is 220Ω
- (a)
- Why are holes carries present in n-type semiconductor?
- A transistor has low input impedance and high output impendence. Why?
- Why is silicon preferred to germanium in manufacturing semiconductor devices
(b)Study the circuit below of npn transistor
An npn transistor circuit above has ![]() = 0.985 and VBE = 0.3V. If VCC = 16V. Calculate R1 and Rc to place Q point at Ic = 2mA, VCE = 6V
= 0.985 and VBE = 0.3V. If VCC = 16V. Calculate R1 and Rc to place Q point at Ic = 2mA, VCE = 6V
- (a)
- Derive an expression for the output of an operation amplifier as differentiator
- In an integration the feedback capacitor has a capacitance of 0.01μF and a resistor of 10KΩ is connected to an input source of V1 = -1V. If the opamp is biased by + 10V determine the output voltage at time t= 0.5ms and the time taken for the opamp to saturate.
(b) (i) Why NAND and NOR gates are called Universal gates?
(ii)Obtain the truth table for the circuit shown below.
(c)An alarm system is controlled by three sensors, A, B and C. The system sounds it alarm when sensor A and B are on or when sensors B and C are on. Draw the truth table for the system and design its logic gate/
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 60
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 60
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM SIX JOINT EXAMINATION 2023
PHYSICS 2
TIME: 3 HRS , 2023
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists six questions
- Answer FIVE (05) questions,
- Each question carries twenty (20) marks.
- All necessary rules and regulations as per NECTA requirements apply.
- The following constants may be used:
- Acceleration due to gravity g = 9.8ms-2
- Density of water ꝭwater = 1000kgm-3
- Electronic charge, е =1.6 x 10-19 C
- Speed of light in vacuum, C = 3.0 x 108 m/s
- Universal gas constant, R = 8.31J/mol K.
- Mass of electron at rest, Me = 9.1 x 10-31kg
- Avogadro’s constant, h = 6.63 x 10-34Js
- Atomic mass unit (a.m.u) = 931 mev = 1.661 x 10-27kg
- Surface tension of water = 7.0 x 10-2Nm
- Surface tension of soap solution = 2.5 x 10-3Nm
- Young modulus of steel = 2.0 x 1011Nm-2
- Permittivity of free space,
- Permeability of free space, μ0 = 4π x 10-7 Hm-1
- Reydbergs constant = 1.0974 x 107 m-1
- Specific heat capacity of water, C = 1calg-1k-1
1. (a) (i) Distinguish between static pressure, dynamic pressure and total pressure when applied to streamline or lamina fluid flow and write down expressions at a point in the fluid in terms of the fluid velocity v, the fluid density , pressure p, and the height h of the point with respect to a datum. (03 marks)
(ii) The static pressure in a horizontal pipeline is 4.3 x 103 Pa, total pressure is
4.7 x 104 Pa and the area of cross-section is 20 cm2. The fluid may be considered to be incompressible and non-viscous and has a density of 1000 kgm-3. Calculate the flow velocity and the volume flow rate in the pipeline. (04 marks)
(b) (i) Write a mathematical implication of Newton’s law of viscosity and hence deduce the dimensions of the coefficient of viscosity. (02 marks)
(ii) Calculate the terminal velocity of the raindrops falling in air assuming that the flow is laminar, the raindrops are spheres of diameter 1 mm and the coefficient of viscosity is 1.8 x 10-5Nsm-2 (04 marks)
(c) (i) Water flows past a horizontal plate of area 1.2m2. If its velocity gradient and coefficient of viscosity adjacent to the plate are 10 s-1 and 1.3 x 10-5 Nsm-2 respectively, calculate the force acting on the plate. (03 marks)
(ii) A horizontal pipe of cross section area of 10 cm2 has one section of cross sectional area 5 cm2. If water flows through the pipe, and the pressure difference between the two sections is 300 Pa, how many cubic metre of water will flow out of the pipe in 1 minute? (04 marks)
2. (a) Define the following terms
- Free surface energy (01 mark)
- Capillarity (01 mark)
- Angle of contact (01 mark)
(b) A steel wire AB of length 60 cm and cross section area 1.5 x 10-6 m2 is attached at B to copper wire BC of 39 cm and cross sectional area 3.0 x 10-6 m2. If the combination of the two wires is suspended vertically from a fixed point at A, and supports a weight of 250N at C, find the extension (in millimeter) of the
(i) Steel wire (04 marks)
(ii) Copper wire (04 marks)
(c) (i) Based on the kinetic theory of gases, determine the average translational kinetic energy of air at a temperature of 290K (04 marks)
(ii) Water rises to a height h inside a clean capillary tube of radius 0.2 mm when the tube is placed vertically inside a beaker of water. Calculate h, if surface tension of water is 7.0 x 10-2Nm-1. If the tube is now pushed into the water until 4 cm of its length is above the surface, describe and explain what will happen. (05 marks)
3. (a) (i) Explain two properties of media for the propagation of mechanical wave.
(02 marks)
(ii) Two similar sonometer wires of the same material produce 2 beats per second. The length of one is 50cm and that of the other is 50.1cm. Calculate the frequencies. (04 marks)
(b) (i) Explain the two types of Doppler shift as applied in Doppler effect in light waves.
(02 marks)
(ii) A car travelling at 10m/s sounds its horn, while has a frequency of 500Hz and this is heard in another car which is travelling behind the first car, in the same direction, with a velocity of 20m/s. The sound can also be heard in the second car by reflection from a bridge ahead. What frequencies will the drive of the second car hear? (04 marks)
(c) (i) Give any three applications of air wedge (03 marks)
(ii) Air wedge film is formed by placing aluminum foil between two glass slides at a distance of 75cm from the line of the slides. When the air wedge is illuminated normally by light of a wavelength 5.6×10-7 m to the line of contact which has a separation of 1.2mm. Calculate the angle of the wedge and the thickness of the foil. (05 marks)
4. (a) (i) Vehicle carrying inflammable materials usually have metallic ropes touching the ground during motion why?. (02 marks)
(ii) A square of side length 10 cm has four charges placed at its corners. Clockwise from the top right as viewed from above these are 5, −10, 6 and 3 nC. Determine the electric potential at the centre of the square. Assume the medium is air.
(04 marks)
(b) (i) What do you understand by the term Gaussian surface (01 mark)
(ii) The flux of the electric field, through the closed surface S', is found to be four times that through the closed spherical surface S (figure below). Find the magnitude of the charge Q. Given ![]() =1µC,
=1µC, ![]() =-2µC and
=-2µC and ![]() =9.854µC.
=9.854µC.
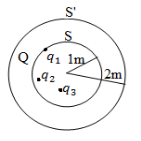 (04 marks)
(04 marks)
(c) (i) Define the term time constant and show that its unit is seconds. (02 marks)
(ii) Derive an expression for capacitance of concentric spherical capacitor of inner and outer radii a and b respectively, hence find the capacitance if a=9cm and b=10cm.
(03 marks)
(iii) A capacitor of 8µF capacitance is connected to a d.c source through a resistance of 1mega ohm. Calculate the time taken by the capacitor to receive 95% of final charge. How long will it take for the capacitor to be fully charged? (04 marks)
5. (a) Discuss the different among ferromagnetic, paramagnetic and diamagnetic substance. (04 marks)
(b) Explain why it is desirable to use hard ferromagnetic materials to make permanent magnet. (03 marks)
(c) A circular coil X of radius 0.02m and turns 100 is placed co- axially at the centre of another circular coil Y of radius 0.2m and turns 1000.
(i) Find mutual inductance of the coils (05 marks)
(ii) If current in Y changes from 7A to 5A in 4x 10-2s, what is the e.m.f induced in X
(03 marks)
(d) Derive energy per unit volume stored in solenoid in terms of permeability of free space and flux density. (05 marks)
6. (a) (i) Define the terms cut off potential (stopping potential) and threshold frequency in photoelectric effect (02 marks)
(ii) Explain briefly how classical theory could not explain the phenomenon of photoelectric effect (02 marks)
(b) Light from a discharge tube containing hydrogen atoms falls on the surface of sodium. The kinetic energy of the fastest electrons emitted from sodium is 0.73eV. the work function for sodium is 1.82ev
Find:
- The energy of the photons causing the photoelectric emission.
(03 marks)
- The quantum numbers of the two levels involved in the emission of these photons. ( 04 marks)
- The change in the angular momentum of the electron in the hydrogen atom in the above transition. (02 marks)
(iv) The recoil speed of the emitting atom assuming it to be at rest before the transition (ionization energy of hydrogen is 13. 6ev). (02 marks)
(c) Draw suitable graphs to show the variation of photoelectric current with collection plate’s potential for
(i) a fixed frequency but different intensities L1>L2>L3 of radiation
(02 marks)
(ii) a fixed intensity but different frequencies, f1> f2>f3 of radiation
(03 marks)
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 50
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 50
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM SIX JOINT EXAMINATION 2023
PHYSICS 1
TIME: 3 HRS 2023
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
1. This paper consists of sections A and B
2. Answer all seven (07) questions from section A and any two (02) questions from section B
3. Write your name on every page of your answer sheet.
4. Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
5. Marks for each question or part thereof are indicated at the end of each question
6. The following information may be useful
a) Acceleration due to gravity g = 9.8 ms-1
b) Gravitational constant G = 6.7 X 10-11 Nm-2kg-2
c) Density of water = 1000 kgm-3
d) Radius of the earth = 6400 km
e) Atomicity for ideal gas = 1.67
f) Electronic charge e = 1.69 x 10-19C
g) Universal gas constant R = 8.31 Jmol-1K-1
h) Stefan’s constant δ = 5.7 X 10-8 wm-2K-1
i) Mass of the earth = 6 x 1024kg
J) The solar constant = 1400 Wm-2
SECTION A
Answer all questions from this section. (70 marks)
1.(a) (i) Define the term accuracy and precision of a measurement. (01 mark)
(ii) The following measurements were taken by the students for the length of a piece of rod 21.02, 20.99, 20.92, 21.11 and 20.69m. Basing on error analysis, find the percentage error associated with this measurement. (04 marks)
(b) (i) State the principle of homogeneity of a physical quantity. (01 mark)
(ii) Mention two physical quantities whose dimension is ML2T-1. (01 mark)
(iii) The velocity V of sound wave depends on Elasticity, E of a material and density ρ of the medium. By using dimension analysis, find the expression of V interms of E and ρ(03 marks)
2. (a) (i) State the principle of conservation of linear momentum. (01 mark)
(ii) Give two differences between elastic and inelastic collision. (01 mark)
(iii) A particle of mass 5M moving with a speed V explodes and spreads into two pieces with masses of 2M and 3M. The lighter piece continues to move in the original direction with a speed of 5V relative to the heavier piece. What is the actual speed of the lighter piece if V = 100ms-1(03 marks)
(b) A basket ball is released from player’s hands with a speed of 8m/s at an angle of ἁ above the horizontal so as to land in the centre of the basket, which is 4m horizontally from the point of release and the vertical height of 0.5m above it. And taking g = 10ms-2
(i) Show that ἁ satisfies the equation 5![]() α - 16 tanα + 7 =0 (02 marks)
α - 16 tanα + 7 =0 (02 marks)
(ii) Use the equation to find the angle ἁ and the time taken from the point of projection until it lands in the centre of the basket. (03 marks)
3. (a) (i) Using the same axis plot the graph of K.E, P.E, and Total energy against time for a particle performing simple harmonic motion. (1.5 marks)
(ii) The length of a simple pendulum executing simple harmonic motion is increased by 21%. What is the percentage increase in the periodic time of the pendulum?
(3.5 marks)
(b) (i) State two points which differentiate between vertical and horizontal circular motion. (02 marks)
(ii) A road curve is banked so that there is no side slip on the passengers in the car which takes the curve at 20m/s speed. Find the angle of banking for circular curve making an angle of ![]() turn in a distance of 628m along the road.(03 marks)
turn in a distance of 628m along the road.(03 marks)
4. (a) (i) State any three essential conditions for a satellite to appear stationary.
(1.5 marks)
(ii) The Earth may be considered to be a sphere of radius 6.4 x 10 6km and its mass of 6 x 1024kg concentrated at its centre. A satellite of mass 650 kg is to be launched from the equatorial and put into geostationary orbit. Determine the increase in gravitational potential energy of the satellite during its launch from the Earth’s surface to geostationary orbit. Suggest the advantage of launching a satellite from the equatorial in the direction of rotational of the Earth. (3.5 marks)
(b) (i) State the parallel axis theorem and perpendicular axis theorem.(02 marks)
(ii) The moment of inertia of a disc about an axis through its edge and perpendicular to the plane is 24 kgm2. Calculate the moment of inertia of the disc about its diameter. Given that ![]() =
=![]() . (03 marks)
. (03 marks)
5. (a) (i) Explain what is meant by temperature gradient. (01 mark)
(ii) An ideally lagged compound bar 25cm long consists of a copper bar 15cm long joined to an alluminium bar 10cm long and of equal cross section area. The free end of the copper is maintained at 1000C and the free end of alluminium at 00C. Calculate the temperature gradient in each bar when steady state conditions have been reached. (03 marks)
(b)(i)State Stefan’s law of black body radiation. (01 mark)
(ii) A blackened metalsphere of diameter 10mm is placed at the focus of a concave mirror of diameter 0.5m directed towards the sun. If the solar power incident on the mirror is 1600Wm-2, calculate the maximum temperature which the sphere can attain. State the assumptions you make.(05 marks)
6. (a) Give one practical example of each of the following;
(i) a process in which heat is supplied to a system without causing any change in temperature. (01 mark)
(ii) a process in which no heat enters or leave the system but the temperature changes. (01 mark)
(b) (i) Why is the energy needed to raise the temperature of a given mass of a gas by a certain amount greater if the pressure is kept constant then if the volume is kept constant. (02 marks)
(ii) Derive an expression for the difference between the molar heat capacities of a perfect gas at constant pressure and at constant volume. (03 marks)
(c) 5 moles of hydrogen, initially at S.T.P are compressed suddenly so that its temperature becomes 4000C. Find
(i) The work done on the gas (1.5 marks)
(ii) The increase in internal energy of the gas. (1.5 mark)
7. (a)
SECTION B (30 marks)
Answer two (02) questions from this section
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 49
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 49
PRESIDENTS OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM SIX JOINT EXAMINATION 2023
PHYSICS 3
TIME: 3.20 HRS -2023
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
1. This paper consists of three (3) questions.
2. Answer all the questions.
3. Calculations should be clearly shown.
4. Question 1 carries 20 marks while questions 2 and 3 carries 15 marks each.
5. All answers must be written in the answer booklet(s) provided.
6. Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
7. Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
8. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
9. Use the following:
- Pie ![]()
- In this experiment you are required to determine the relative density of a solid provided.
Proceed as follow;
- (i) Measure the mass of the metre rule and record its value.
(ii) Set up the apparatus as shown in figure 1.Balance the metre rule on the knife edge, when the solid, Mo is suspended in air at a distance, d (cm) from zero end of the rule.
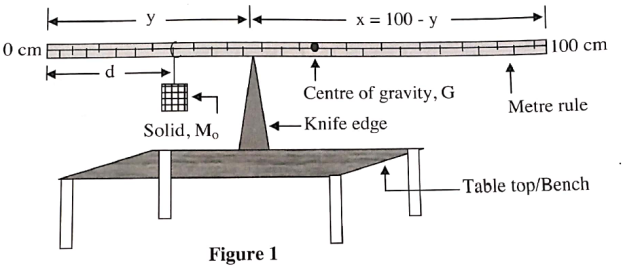
- Measure the distance, y(cm) and x(cm) of the knife edge from each end of the ruler; y being the distance from the zero end. Repeat four other values of, d less than 50cm. Tabulate your results
- Fill the beaker with water then repeat the procedure in parts (a) and (b) when the solid is completely immersed in water. Tabulate your results
- Plot the graphs of x-y against y-d for each set of observations on the same sheet of the graph paper
- Find the gradient of each graph
- Calculate the;
- Mass of the solid
- Relative density of the solid
- State two sources of errors and its precautions taken in performing this experiment.
- You are required to plot the cooling curves for hot water in a calorimeter with the calorimeter about
- Half full of water
- Two-third full of water
Proceed as follows;
Half fill a weighed calorimeter with water so that the temperature immediately after this operation is about 650C. Observe the temperature of the contents at interval of two minutes as if cools over a temperature range 600C to 450C, weigh the calorimeter with water after the experiment.
Repeat the procedure with the calorimeter about two- thirds full of water
- Plot both cooling curves on the same frame of axes and obtain from them the ratio of the time taken to cool over the same temperature interval, when the temperature interval involved is
- 600C - 500C (ii) 600C - 450C (iii) 550C – 450C
- Calculate the total ratio of the total thermal capacities in the two experiments. (Take specific heat capacity of calorimeter as; CCU = 400 Jkg-1k-1,
CAL = 890 Jkg-1k-1. Specific heat capacity of water, CW = 4200 Jkg-1k-1.
- You are required to determine the resistance of the wire W per unit length and the length of the wire wound on a non conducting material. Proceed as follow;
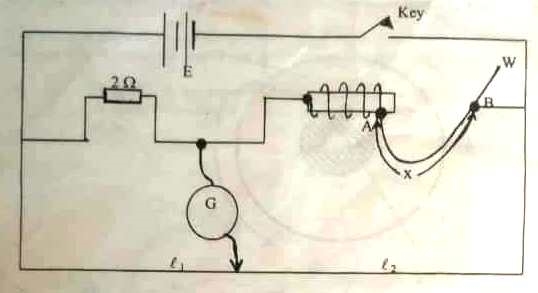
- Connect the circuit as shown in the figure.3 above, E is a 3V battery and G is a centre-zero galvanometer. Place a 2Ω resistor on the left hand gap of the metre bridge and connect the wire provided to the right hand gap of the metre bridge.
- Determine the value of the resistance R of the wire W when AB=x= 60cm. Terminal B can be adjusted to allow different values of x of the wire W.
- Repeat the experiment in (b) above, for values of R when x= 50cm, 40cm, 30cm, 20cm, 10cm. Tabulate your results for values
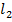 , x and R.
, x and R. - Plot graph of R against x
- Calculate the slope S of the graph. Measure the diameter d, of the wire W. Hence find the resistivity of wire W
- Use the relation R = S( x +ℓ) to determine the value of ℓ where ℓ is the length of the wire wound permanently on a (wooden block) non-conducting material
- Determine the value of x- intercept. What does it represent?
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 48
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 48
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
FORM SIX EXAM SERIES
PRE-NATIONAL
PHYSICS-2
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3:00 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. This paper consists of THREE sections, A, B and C
2. Answer a total of TEN (10 ) questions including FOUR questions from section A, THREE questions from section B and THREE questions from section C
3. Marks for each question or parts of question are thereof indicated in small braces
4. Tick each question attempted in a relevant box in a table below
5. Non- programmable scientific calculators may be used.
6. Where necessary the following scientific constants may be used in your calculations.
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8m/s2
Pie, ![]() = 3.14
= 3.14
Radius of the earth, re= 6400km
Distance of the earth from the sun Ro = 1.5 x 108km
Universal gravitation constant, G= 6.67 x 10-11Nm2kg-2
Moment of inertia for a hollow cylinder ![]()
Mass of an electron, me= 9.1 x 10-31kg
Electronic charge e-= 1.6 x 10-19C
Latent heat of vaporization of water Lv = 2.26 x 106JKg
SECTION A
Answer only FOUR (4) questions from this section
1. (a)(i) What is meant by ‘dimension of a physical quantity?’ (01Mark)
(ii) In the gas equation![]() . Each symbols carry its usual meaning.Find the dimensions of" a" and "b"(02Marks)
. Each symbols carry its usual meaning.Find the dimensions of" a" and "b"(02Marks)
(b)(i)Check correctness (consistency) of equation below where each letter carries its usual meaning.
Q/t=6×pie×n×r×V.(03Marks)
(ii) The frequency ![]() of a note produced by a taut wire stretched between two supports depends on the distance
of a note produced by a taut wire stretched between two supports depends on the distance ![]() between the supports, the mass per unit length of the wire,
between the supports, the mass per unit length of the wire, ![]() and the tension
and the tension ![]() . Use dimensional analysis to find how
. Use dimensional analysis to find how ![]() is related to
is related to ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() (04 Marks)
(04 Marks)
2. (a)(i) What are the three assumptions in treating projectile motion?(1.5Marks)
(ii) Discuss any three applications and three limitations of projectile motion (1.5Marks)
(b) A missile is projected from point A on a level ground at speed 40m/s at 60o to the horizontal towards point B which is at 100m apart from A at the same time antimissile at B is projected towards A with speed Vo at angle θ to the horizontal. If the two collide at 40m from A. Determine the:-
(i) time taken for the two to collide in air (04Marks)
(ii) Velocity of antimissile, Vo and its angle of projection, θ (03Marks)
3. (a)(i) State Newton’s second law of motion (01Mark)
(ii)A train of mass 200,000kg moves at constant speed of 72km/h up a straight inclined plane against a frictional force of 12800N.The inclined is such that the train rises vertically 1m for every 100m travelled along the plane. Find the rate of increase per second of the potential energy of the train and the necessary power developed by the train (04Marks)
(b) Rockets are propelled by ejection of the products of the combustion of fuel. Consider a rocket of total mass mo travelling at a speed V in a region of space where gravitational forces are negligible
(i) Supposing the combustion products are ejected at a constant speed Vex relative to the rocket, show that the fuel‘burn’ which reduces the total mass mo of the rocket to m results in an increase in speed of the rocket from U to V
Show that:-
![]() (03Marks)
(03Marks)
(ii) Supposing that 2.1 x 106Kg of fuel are consumed during a ‘burn’ lasting 1.5 x 102seconds and given that there is
a constant force on the rocket of 3.4 x 107N during this burn. Calculate Vex and increase in speed resulting from the burn if mo = 2.8 x 106Kg
(02Marks)
04.(a)Astoneofmass150gmovesinaverticalcircleontheendoflengthofastring.Theradiusofthecircleis70cmandthespeedofthestoneatthetopmostpointis3.5m/s.Fortheinstantatwhichthestonepassesthroughthehighestpoint.Find
(i)The resultant force on the stone(03Marks)
(ii)The tension in the string(03Marks)
(b) An object of mass 10Kg is whirled round a horizontal circle of radius 4m by a revolving string inclined to the vertical. If the uniform speed of the object is 4.76m/s. Calculate
(i) the tension in the string(02Marks)
(ii) the angle of inclination of the string to the vertical
(02Marks)
05. (a)(i) Name two conditions necessary for a particle to execute S.H.M
(02 Marks)
(ii) Explain why motion of simple pendulum is NOT strictly S.H.M.?(02Marks)
(b) Asmallmassof200gattachedtooneendofspringandproducesanextensionof15mm.Themassisnowsetintooscillationofamplitude10mm.Find the:-
(i) Maximum kinetic energy (03Marks)
(ii) potential energy of the spring when the mass is 5mm below the centre of oscillation. (03Marks)
06.(a)(i) A recording disc rotates steadily at 45rev/min on a turn-table.When a small mass of 0.02kg is droped gently on to the disc at a distance of 0.04m from its axis and sticks to the disc, the rate of revolution falls to 36rev/min. Calculate the moment of inertia of the disc about its centre.(04Marks)
(ii)State the principle you have applied in6(a)(i)above.(02Marks)
(b) A hollow cylinder of radius 5cm and mass 10kg rolls without slipping in an inclined plane inclined at 30o, calculate
(i) the total energy of the sphere
(02 Marks)
(ii) the linear and angular acceleration (02Marks)
SECTION: B
Answer only three questions from this section
07.(a) (i) With the aid of a diagram describe the working of a platinum resistance thermometer
(02 Marks)
(ii) Name any four disadvantages of pyrometer (02Marks)
(b) (i) Three bars A,B and C of same cross sectional area and of lengths 50cm,50cm and 40cm respectively were joined to form Y-shape. If the free ends of A and B are maintained at 10oC each while the free end of C is maintained at 100oC.Determine the temperature gradient of each bar at stead state conditions. Given that the thermal conductivity of A is twice that of B and thrice that of C. (03Marks)
(ii) Show that for a perfectly lagged conductor(bar) the rate of heat flow per unit volume is given by
![]()
where k is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material conductor (03Marks)
8. (a) Briefly explain why:-
(i) Stainless steel cooking pans are preferred with extra copper bottom?(02Marks)
(ii) On a winter night you feel warmer when clouds cover the sky than the sky is clear(02Marks)
(b) An aluminium foil of relative emittance 0.2 is placed between two concentric spheres at temperatures 300K and 200K respectively. Calculate:-
(i)The temperature of the foil after the steady state condition is reached(03Marks)
(ii)The rate of energy transfer between one of the spheres and the foil ( Stefans constant = 5.67×10 ^ -8 unit)(03Marks)
09. (a)(i) What is meant by drift velocity of electrons?(01Marks)
(ii) Explain why an electric bulb turns on soon as the switch is closed though the drift velocity of electrons is small(02 Marks)
(b)(i) Calculate drift velocity of electrons through copper wire from the following data
-Current through the wire, I = 2A
-Cross-sectional area of copper wire, A = 2mm2
-Avogadro’s number, NA = 6.02 x 1023mol-1
-Density of copper, ρ = 8.9 x 103kg/m3
-Molar mass of Copper, Cu = 63.5gmol-1
(03 Marks)
(ii) Show that the electron mobility µe is given by ![]() where each letter carries its usual meaning
where each letter carries its usual meaning
hence Using derived equation above calculate relaxation time, ![]() if electron mobility,
if electron mobility, ![]() (04 Marks)
(04 Marks)
10.(a)(i)Derive an expression for resonant frequency in L C parallelcircuit?
(02Marks)
(ii) A coil of inductance 8 Micro Henry is connected to a capacitor of capacitance 0.02 Micro Farrad. To what wavelength is this circuit turned?(03Marks)
(b)A 1200pF capacitor is charged by a 500V battery. It is disconnected from the battery and is connected to a 75mH inductor. Calculate the:-
(i)Initial charge on the capacitor(02Marks)
(ii)Total energy oscillating in the system(03Marks)
SECTION: C
Answer only three questions from this section
11.(a)(i) Explain briefly the formation of potential barrier across the PN junction diode
(02Marks)
(ii) Applying the concept of doping, explain how a free electron and a positive charge can be created in a semiconductor crystal
(03Marks)
(b) An NPN transistor is connected in a common emitter mode in which a collector supply is 8V and the voltage drop across the load resistance of 8Kilo Ohms connected in the collector is 0.8V. If the current amplification factor is 25. Determine :-
(i) Collector Emitter voltage and base current if the input resistance of a transistor is2 kilo Ohms(03Marks)
(ii) power gain
(02Marks)
12.(a) (i) Explain what is an operational amplifier(02Marks)
(ii) State Three assumptions made for analyzing Ideal OP-AMP?(03Marks)
(b)(i)With the aid of circuit diagram,derive an expression for the gain of non inverting amplifier(03Marks)
(ii)With the help of circuit diagram explain how an opamp can be used as a voltage comperator.(02Marks)
13. (a) Give symbols, expressions and truth tablesfor each of the following logic gates:-
(i) NAND gate
(03Marks)
(ii) Exclusive NOR gate
(02Marks)
(b) (i)Explain why is NAND gate considered as a basic building block for a variety of logic circuits?(02Marks)
(ii) Draw a simplified logic circuit from the following truth table.
| A | B | C | D | OUTPUT |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
(03Marks)
14.(a) (i)Distinguish between Amplitude modulation and frequency modulation and give two advantages of frequency modulation.
(02Marks)
(ii)Draw a block diagram to show basic components ofa transmitter and a receiver and explain the functions of each components for both cases.(03Marks)
(b) The amplitude modulated broadcast band ranges from 450KHZ to 1200KHZ. If each station modulates with audio frequencies up to 5.5KHZ. Determine the;-
(i)Bandwidth needed for each station
(03 Marks)
(ii) Total bandwidth available
(02Marks)
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 47
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 47
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
MOCK EXAMINATION SOUTHERN ZONE
(MTWARA AND LINDI )
131/2 PHYSICS 2
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3:00 HOURS
PHYSICS
Instructions
- This paper consists of six (6) questions.
- Answer any five (5) questions
- Each question carries twenty (20) marks
- Non-programmable calculators and formula may be used.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklets(s)
- The following information may be useful
- Acceleration due to gravity, g=9.8m/s2
- Pie
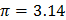
- Density of mercury = 13.6 x 103kg/m3
- Density of water = 103kg/m3
- Charge of electron,
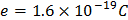
- Speed of light,
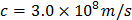
- Plank’s constant,
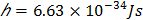
- 1
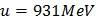
- Permeability of free space,
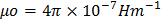
- Rydberg’s constant,
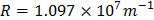
- Young’s modulus of copper,
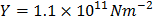
- Young’s modulus of steel = 2 x 1011Nm-2
- Mass of electron, me =
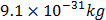
- Permittivity of free space,
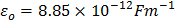
- Velocity of sound in air, = 344m/s
-
- (a)Distinguish between streamline and Turbulent flow in liquids.
(b)Give clear explanations of the followings:
- The speed of innermost layer of a whirlwind is alarmingly high.
- A flag flutter, when strong winds are blowing on a certain day.
- The accumulation of snow on an aeroplane wings may reduce the lift
- Children are told to avoid standing too close to rapidly moving train because they might get sucked under it, is this possible? Explain
(c)A Venturi meter used to measure flow rate in pipe is installed in a horizontal water pipe as shown in the diagram, below. The pipe has a circular cross section with diameter D1 in the first segment and D2 in the second segment with D2< D1 the density of water is ![]() . The volume flow rate in the pipe is R measured in m3/s.
. The volume flow rate in the pipe is R measured in m3/s.
- Obtain an expression of the speed of flow V1 in the first section of the pipe in terms of R and D1.
- What is the speed of flow V2 in the second section of the pipe?
- Find an expression for pressure difference between point 1 and point 2
- What is the difference h in water level in two tubes expressed in terms of R, D1 and D2
- if the volume flow rate through the pipe is 10-3m3/s and the pipe has a diameter 0.1m at point 1 given the density of water 1000kg/m3 and viscosity of water is 10-3/m2, determine the type of flow in the pipe
(d)(i)State two factors which determine the magnitude of viscous force.
(ii)Identify two limitations of applying stokes law in fluids motion.
- (a)(i)In an experiment it was found that the string vibrate in three loops when 8g were placed on the scale pan. What mass must be placed on the pan to make the string vibrate in six loops. (Neglect the mass of the string and the scale pan)
(ii)two sitar strings A and B playing the note “dha” are slightly put of tune and produces beats of frequency 5Hz. The tension of the string B is slightly increased and the beat frequency is found to reduce to 3Hz. What is the original frequency of B if the frequency of A is 427Hz?
(b)(i) What are sound waves?
(ii)A small explosion is set off on a steel railway line and the observer L, 1km away with one ear to the rail hears two reports. Find the interval between the two reports if air pressure is 105Pa.
(c)(i)Give the meaning of the terms “node” and “antinode” as applied to stationary waves.
(ii) A sonometer wire of length 76cm is maintained under a tension of 40N while an alternating current is allowed to pass through it. A horse shoe magnet is now placed with its poles above and below the wire at its mid-point and the resulting force setting the wire in resonant vibration. If the density of wire is 8800Kg/m3 and its diameter is 1mm, what is the frequency of alternating current?
(d)Two trains moving toward each other along parallel tracks whistled each other at a frequency of 400Hz. If one train travels at a 25m/s what must be the speed of the other train so that a stationary observer at their point of convergence hears 5 beats per second.
- (a) Explain the following
- Rain drops hit the ground with less force than they should
- Oil is poured to calm sea waves
- The new earthen pots keep water cooler than the old ones.
(b)A soap bubble in a piston chamber of pressure has a radius R. If the piston is pulled out until the radius of a soap bubble doubles.
- Show that the new pressure inside the chamber is given by
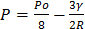 where
where 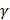 is the surface tension of soap solution.
is the surface tension of soap solution. - If the piston is compressed until the radius is halved, show that the new pressure inside the chamber is
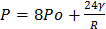
(c)A 2.0m light rigid rod is suspended from the ceiling by two vertical wires A and B each having a natural length of 1.0m attached to each end of the rod. A is a copper wire with Young’s modulus 1.24 x 1011N/m2 and diameter 1.60mm and B is the brass wire of Young’s modulus 9 x 1010N/m2 and diameter 1.0mm. A 80kg mass is attached to the midpoint of the rod.
Calculate:
- The tension in each wire assuming the rod is horizontal
- The consequent extension of A
- The angle the rod makes with the horizontal
(d)(i)Why are bridges declared unsafe after long use.
(ii) Would you expect rubber band to have larger or smaller force constant than of iron wire? Explain.
- (a)(i) The electrostatic force between two protons situated at a distance X from each other is Y Newton. What will be the electrostatic force between two electrons situated at the same distance
(ii)A charge particle is fired with the velocity V making a certain angle with an electric line of force. Will the charge particle move along the line of force?
(b)(i)A boy brings the palm of his hand near the disc of a charged gold leaf electroscope. The leaves of electroscope are observed to collapse slightly. But when the boy moves his hands away from the gold leaf electroscope, the leaves resume their original position. How do you explain the behavior of the leaf?
(ii)Two charges of 10-9C each are 8cm in air. Calculate the magnitude and direction of forces exerted by these charges on a third charge of 5 x 10-9C which is 5cm from each of the first two charges. Calculate also the resultant force for all charges.
(c)(i)Explain why capacitors are important.
(ii)Two spherical conducting shells of radii 5cm and 10cm are maintained at 300V and 600V respectively. The two cells are joined together by a wire. Calculate the energy lost assuming that the two shells are 50mm apart.
(iii)Two large horizontal metal plates are 2cm apart in vacuum. The upper plate is maintained at a positive potential relative to the lower plate so that the field strength between them is 2.5 x 105Vm-1. Calculate the potential difference between the plates and the speed on reaching the upper plate of an electron liberated from rest at the lower plate.
(d) Two capacitors of capacitance 15![]() and 20
and 20![]() are connected in series to a 600V d.c Supply. Calculate:
are connected in series to a 600V d.c Supply. Calculate:
- Charge on each capacitor
- Potential difference across each capacitor
- (a)Write down the statement of ampere’s circuit law and write the corresponding equation.
(b)Using diagram describe in what way is the behavior of diamagnetic material different from that of paramagnetic material when kept in an external magnetic field.
(c)Explain by giving reasons for the following:
- Increasing the current sensitivity of galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity.
- A galvanometer cannot be used to measure current in a given circuit.
- No force is experienced by a stationary charge in a magnetic field
- No two magnetic lines of force intersect each other.
(d)The current flowing through an inductor of self-inductance L is continuously increasing. Plot a graph showing a variation of:
- Magnetic flux versus current
- Induced emf versus
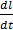
- Magnetic potential energy stored versus the current.
(e)Starting from expression for energy ![]() stored in solenoid of self-inductance L to build up a current I, Obtain the expression for magnetic energy in terms of magnetic field B, area A and length L of solenoid having n number of turns per unit length.
stored in solenoid of self-inductance L to build up a current I, Obtain the expression for magnetic energy in terms of magnetic field B, area A and length L of solenoid having n number of turns per unit length.
- (a)Write the relation for binding energy in MeV of a nucleus of mass
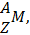 atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) in terms of masses of its constituents-Neutrons and protons.
atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) in terms of masses of its constituents-Neutrons and protons.
(b)Draw a plot of BE/A versus mass number A for 2 ≤ A ≤ 170. Use this graph to explain the release of energy in the process of nuclear fusion of two light nuclei.
(c)A star initially has 1040 deuterons. It produces energy via process:
![]()
![]()
Where the masses of the nuclei are ![]()
![]()
If the average power radiated by a star is ![]() how long will deuteron supply of the star is exhausted.
how long will deuteron supply of the star is exhausted.
(d)Read the following passage and answer the following questions:
A nucleus at rest undergoes a decay emitting an α-particle of de Broglie wavelength 5.76 x 10-15m. The mass of daughter nucleus D is 223.610amu and the mass of an α-particle is 4.002amu. Take 1amu = 1.656 x 10-27Kg and Plank’s constant h=6.63 x 10-34Js
- What is the momentum of the α-particle in Kgm/s.
- Calculate the total kinetic energy of two particles.
- Calculate the mass of the parent nucleus.
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 46
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 46
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
MOCK EXAMINATION SOUTHERN ZONE
(MTWARA AND LINDI)
131/2 PHYSICS 2
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3:00 HOURS
PHYSICS 2
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of six (6) questions.
- Answer any five (5) question carries twenty (20) marks.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are NOT allowed in the examination room.
- Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
- The following information may be useful.
- Acceleration due to gravity, g=9.8m/s2
- Specific gravity of alcohol = 0.8
- Density of air
 air = 1.2kg/m3
air = 1.2kg/m3 - Refractive index of water,
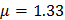
- Speed of light, c=3.0 x 108m/s
- Avogadro’s Number, NA=6.02 x 1023mol-1
- Relative permittivity of free space
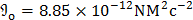
- Density of water
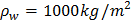
- (a)Briefly explain the following
- Why water flows faster than honey?
- Why do air bubbles in water rise up?
(b)Calculate the speed at which the velocity head of a stream of water is equal to 0.56m of Hg.
(c)(i)A pilot tube is mounted on an aeroplane to measure the speed of the plane. The tube contains alcohol and shows a level difference of 40cm. What is the speed of the plane related to air?
(ii) Identify three differences between solid friction and fluid friction
(d)Bernoulli’s theorem can be written in the form of ![]() = constant. What does each term in the left hand side of the equation represent?
= constant. What does each term in the left hand side of the equation represent?
- (a)(i)Define the term surface tension in terms of surface energy.
(ii)Why is it difficult to fill mercury in the glass tube of a mercury thermometer?
(iii)Often in the early morning we see very minute water or dew drops being spread on the leaves of some trees. On slightly lowering these leaves, these drops slide over the leaves without breaking or spreading. Briefly explain this explanation
(b) A film of water is formed between two straight parallel wires each 10cm long at a separation of 0.5cm. Calculate the work required to increase 1mm distance between the wires. Surface tension of water is 72 x 10-3N/m
(c)Two spherical soap bubbles, coalesce to form a single bubble. If V is change in volume of the contained air and A s the change in total surface area, then show that 3PaV + 4![]() a=0, where
a=0, where ![]() is the surface tension and Pa is the atmospheric pressure.
is the surface tension and Pa is the atmospheric pressure.
- (a)(i)Why is a given sound louder in a hall than in the open?
(ii) Why does an empty vessel produce more sound than a filled one?
(b) The wavelength of yellow sodium line 5896![]() emitted by a star is red shifted to 6010A°. What is the component of the star’s recessional velocity along the line of sight? For small recessional speeds, you may use a formula for Doppler effect analogous to that of sound (speed of light is 3 x 108m/s)
emitted by a star is red shifted to 6010A°. What is the component of the star’s recessional velocity along the line of sight? For small recessional speeds, you may use a formula for Doppler effect analogous to that of sound (speed of light is 3 x 108m/s)
(c)The equation of a standing wave is given by y(x, t) = 12![]() where x and y are in cm and t in second. Find
where x and y are in cm and t in second. Find
- Frequency and wavelength
- Velocity and amplitude of the progressive wave.
- (a)(i)State any four assumption of kinetic theory of gases.
(ii)How many molecules you breathe in litre breath of air?
(b)Nine particles have speed of 5, 8, 12, 12, 14, 14, 17 and 20ms-1. Find
- The average speed
- The r.rs speed
- The most probable speed of the particles
(c)(i)Briefly why a hollow shaft is stronger than a solid shaft made of the same equal material?
(ii)Anvils made of single crystal of diamond, with the shape as shown in the figure (mm) are used to investigate behavior of materials under very high pressures. Flat faces at the narrow end of the anvil have a diameter of 0.50mm, and the wide ends are subjected to a compressional force of 50,000N. What is the pressure at the tip of the anvil?
(d)a cube is subjected to a pressure of 5 x 105Nm-2. Each side of the cube is shorted by 1%. Find
- The volumetric strain.
- Bulk modulus of elasticity of a cube material
- (a)
- State Brewster’s law
- Identify three applications of polarized light
- Sunlight is reflected from a calm lake. The reflected light is totally polarized. What is the angle between the sun and the horizon?
(b)A diffraction grating produces a second order maximum at 50.6° to the normal when being illuminated normally with light of wavelength 644nm. Calculate the number of lines per millimeter of the grating.
(c)(i)Differentiate the two main types of diffraction
(ii)Briefly explain two ways in which Young’s experiment can be improved
- (a)(i) State Gauss’s law of electric flux
(ii)A disc of radius 0.10m is oriented with its area vector at 30° to a uniform electric field E of magnitude 2.0 x 10-3NC-1. Calculate the electric flux through the disc.
(b)(i)Distinguish electric potential from electric potential energy.
(ii)Point changes of 3 x 10-9c are located at two vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 20cm. How much work will be done to bring a test charge of 10-9c from infinity up to the third corner of the triangle?
(c)An electron falls through a distance of 1.5cm in a uniform electric field of magnitude 2.0 x 104N/C, figure (yyy). The direction of the field is reversed keeping its magnitude unchanged and a proton falls through the same distance figure (zzz). Calculate the time of fall in each case.
(d)A battery of 10V is connected to a capacitor of capacitance 0.1F. The battery is now removed and this capacitor is connected to a second uncharged capacitor. If the charge distributed equally on these two capacitors, find the total energy stored in the two capacitors. Also compare this energy with the initial energy stored in the first capacitor?
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 45
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 45
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION MOCK EXAMINATION SOUTHERN ZONE (MTWARA AND LINDI
131/2PHYSICS 2
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3:00 HOURSWednesday, 02ndFebruary 2022 p.m
![]()
INSTRUCTIONS
1.This paper consists of six (6) questions.
2.Answer any five (5) questions Each question carries twenty (20) marks.
3.Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are NOT allowed in the examination room.
4.Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
5.Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
6.The following information may be useful
(a)Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8m/s2
(b)Pie, π= 3.14
(c)Speed of light , c= 3×108m/s
(d)Charge of electron, e= 1.6×10−19C
(e)Electron mass ratio(e/m) = 1.8 ×10−11C/kg
(f)Atmospheric pressure = 1.013 ×105Pa (g) Avogadro’s Number,NA= 6.02×1023mol−1(h) Young’s modulus of steel = 2.0×1011N/m2.
(i)Density of soap solution, = 1200kgm−3
(j)Coefficient of viscosity of water, η= 1.0×10−3Nsm−2(k) Boltzmann’s constant, k = 1.38×10−23JK−1.
(l)Surface tension of soap solution = 0.05Nm−1
(m)1u = 931MeV
1.(a)State the principle on which Bernoulli’s theorem is based.(02 marks)
(ii) Why does the speed of a liquid increases and its pressure decreases when a liquid pass through constriction in a pipe? (03 marks)
(b)(i) If two ships are moving parallel and close to each other they experience an attractive force. Why? (02 marks)
(ii)An empty vessel is open at the top has a horizontal capillary tube of length 20cm and internal radius 1.00mm protruding from one of its side wall immediately above the base. Water flows into the vessel at a constant rate of 1.5cm3/s. At what depth does the water level stop rising? (05 marks)
(c)(i) Explain why machine parts are jammed during winter?(02 marks)
(ii)A cylindrical tank with large diameter is filled with water to a depth D= 0.3m. A hole of cross-sectional area of A = 6.5cm2in the bottom of the tank allows water to drain out, what is the drainage rate? At what distance below the bottom of the tank is the cross-sectional area of the steam equal to one half the area of the hole? (Rate should be in m3/s) (06 marks)
2.(a)(i) Why can not two astronauts talk on the moon as they do on earth? (03 marks)
(ii) What is the evidence that sound is a form of energy?(03 marks)
(b)(i) Give two cases in which there is no doppler effect in sound. (02 marks)
(ii)In measuring the blood flow in a patient ultrasound of frequency 5.0MHz is incident at an angle of 30◦to the blood vessel and a doppler shift in frequency of 4.4KHz is observed. If the velocity of ultrasound can be taken as 1.5km/s and the blood vessel is of diameter 1.0mm. Calculate the velocity of the blood flow and the volume rate of blood flow.(05 marks)
(c)(i) Why does sky appear blue?(02 marks)
(ii)What is the angular separation in the first order spectrum between the sodium lines of wavelength 5890Aand 5896˚ Ausing a plane diffraction˚ grating with 6000 lines per cm under normal condition. (05 marks)
3.(a) (i) Mention two factors which may change the value of surface tension. (02 marks)
(ii) An air bubble of radius 1mm is formed at a depth of 5cm inside a large container of soap solution. Calculate the pressure inside the bubble. (04 marks)
(b)(i) Briefly explain why the temperature less than absolute zero (0K) is not possible.(02 marks)
(ii)In a certain region of space there are 5molecules per cm3on an average, the temperature there is 3K. What is the average pressure of this very dilute gas?(04 marks)
(c)The length of wire is cut to half. Why this change has no effect on the maximum load the wire can support? (02 marks)
(ii)A 45kg traffic light is supported with two steel wires of equal lengths and radii of 0.5cm. If the wires make an angle of 15◦with the horizontal, what is the fractional increase in their length due to the weight of traffic light?(06 marks)
4.(a) Two tiny spheres carrying charges 1.5µC and 2.5µC are located 30cm apart. Find the electric field:
(i)At the mid-point of the line joining the two charges.(02 marks)
(ii)At a point 10cm from this mid-point in a plane normal to the line and passing through the mid-point. (03 marks)
(b)An 8µF capacitor is connected in series with 0.5MΩ charge resistor across 200V d.c supply. Calculate;
(i)Initial charging current(02 marks)
(ii)The current and potential difference across capacitor 4seconds after it is connected to the supply.(03 marks)
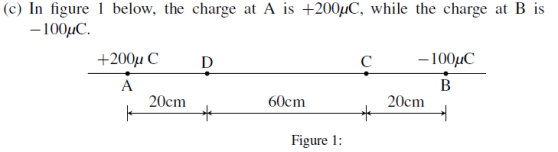
(i)Find the absolute potentials at points C and D. (02 marks)
(ii)How much work must be done to transfer a charge of+500µC from point
C topoint D?(03 marks)
(d)(i) What do you mean by capacitance of a capacitor?(02 marks)
(ii)A 2µF capacitor is fully charged across a 12V battery and connected to an uncharged capacitor. The voltage across it is found to be 3V.what is the capacity of uncharged capacitor? (03 marks)
5.(a) (i) Define the term magnetic flux and give its SI unit. (02 marks)
(ii) Magnetic flux through a coil of resistance 6.5Ω placed with its plane perpendicular to uniform magnetic field varies with time t in second as φ =(3t2+ 5t + 2)mWb. Find the induced current in the coil at t = 10s (04 marks)
(b)(i) What causes sparking in switches, when light is put off.(02 marks)
(ii)A toroid of 1200turns with air core has a radius of 15cm and cross sectional area of 12.0cm2. What is self inductance of a coil? (04 marks)
(c)Why does a metallic piece become very hot when it is surrounded by a coil carrying high frequency of alternating current? (02 marks)
(ii)A coil of 100turns each of an area 20cm2, has a resistance of 5Ω and its end are connected together. A magnetic flux density 3×10−2T is at right angle to the plane of the coil. Find the charge for two cases firstly if this field is removed and secondly if the field is reversed. (06 marks)
6.(a) (i) Define the term Activity and half life. (02 marks)
(ii) The half life of 92U235against alpha decay is 4.5×109years. How much disintegration per second occur in 1g of 92U235(04 marks)
(b)Explain the meaning of the following terms;
(i)Nuclear fusion(02 marks)
(ii)Nuclear fission(02 marks)
(iii)Chain reaction(02 marks)
(iv)Critical mass(02 marks)
(c)In a Rutherford experiment an alpha particle of kinetic energy 8MeV makes a head on collision with a nucleus of sodium![]() .
.
(i)Compare the radius obtained from the collision experiment to that obtained using R = RoA![]() (03 marks)
(03 marks)
(ii)Comment on the differences or similarities of the values obtained.
(01 marks)
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 6
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 6
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
MOCK EXAMINATION SOUTHERN ZONE
(MTWARA AND LINDI )
131/1PHYSICS 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3:00 HOURSMonday, 31stJanuary 2022 a.m
![]()
INSTRUCTIONS
1.This paper consists of section A and B with a total of ten (10) questions.
2.Answer all questions in section A and two (2) questions from section B.
3.Section A carries seventy (70) marks and section B carries thirty (30) marks.
4.Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
5.Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
6.The following information may be useful
(a)Acceleration due to gravity,g= 9.8m/s2
(b)Pie, π= 3.14
(c)Mass of Earth = 6.0 ×1024kg
(f)Radius of the earth, R = 6.4×106m.
(g)Atomic mass of oxygen molecules(O2) = 32u
(h)Universal gas constant, R = 8.31J/mol K
(i)Ratio of specific heat capacities , γ= 1.67
(j)Gravitational constant, G = 6.67×10−11Nm−2kg−2
SECTION A (60 marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1.(a) Three physics students Michael, Mathew and Raphael were taken the measurement of the thread of about 60.00cm lengths at four different times. The results were recorded as follows;
| Student | L1(cm) | L2(cm) | L3(cm) | L4(cm) |
| Michael | 57.50 | 57.49 | 57.49 | 57.48 |
| Matthew | 60.30 | 59.80 | 60.00 | 59.70 |
| Raphael | 60.02 | 60.01 | 60.00 | 60.01 |
(i)Comment about precious and accuracy on three observation from the table.(03 marks)
(ii)Find percentage error for each student(03 marks)
(b)A student while doing an experiment finds that the velocity(V) of an object varies with time t, and it can be expressed as equation of V = Xt2+Yt + Z. If unit of V and t are expressed in terms of SI units, determine the unit of constants X, Y and Z in the given equation. (04 marks)
2.(a) (i) Dust from a carpet can be removed by shaking or beating it. How is it possible? (02 marks)
(ii) Why is it difficult for a fire man to hold a hose, which ejects large amount of water at a high velocity? (02 marks)
(b)Two points A and B are projected at the same time in the same vertical plane.
A is projected at a height of 2m above the ground and making an angle of 30◦ with the horizontal, B is projected with velocity of 30m/s at the ground vertically below A making an angle of 60◦ with the horizontal. If they collide together, Determine
(i)Time taken until they collide(03 marks)
(ii)Horizontal displacement in the part of collision(03 marks)
3.(a) (i) Water in a bucket whirled in a vertical circle do not spill out when whirled fast, but when whirled slowly the water spill out, why? (02 marks)
(ii) A ball is released from a height h along the slope and at the end of a slope moves along a circular track of radius R without falling vertically downwards. Determine the height h in terms of R. (03 marks)
Figure 1:
(b)(i) State one condition for an oscillatory motion to be considered as simple harmonic motion(02 marks)
(ii)A particle executing simple harmonic motion has a velocity of 1.8m/s when passing through its mean position and acceleration at 0.6m from mean position is 2.4m/s2. Find the amplitude and period of oscillation.(03 marks)
4.(a) A flywheel is mounted on a horizontal axle which has a radius of 0.06m. A constant force of 50N is applied tangentially to the axle. If the moment of inertia of the system(flywheel + axle) is 4kgm2, calculate
(i)The angular acceleration of the flywheel (02![]() marks)
marks)
(ii)The number of revolutions that the flywheel makes in 16s assuming that it starts from rest.(02![]() marks)
marks)
(b)(i) If escape velocity from earth for a piece of 1g is 11.2km/s, what would be the escape velocity for an object 100times the mass of original piece?(02 marks)
(ii)Suppose that the radius of the earth was to shrink by 1%, its mass remain the same. What would be the acceleration due to gravity g on the earth’s surface?(03 marks)
5.(a) (i) What is thermometric properties of a material?(02 marks)
(ii) A particular resistance thermometer has a resistance of 30Ω at the ice point, 41.580Ω at the steam point and 34.59Ω when immersed in a boiling liquid. A constant volume gas thermometer gives reading of 1.333 ×105Pa, 1.821 ×105Pa and 1.528 ×105Pa at the respectively three temperatures. Determine the temperature at which the liquid is boiling on the scale of the gas thermometer and on the scale of resistance thermometer.(03 marks)
(b)(i) Why the tile floor feels colder than the wooden floor even though both floor materials are at the same temperature? (02 marks)
(ii)A body cools in 10 minutes from 60◦C to 40◦C. What will be its temperature after next 10minutes? The temperature of the surroundings is 10◦C.(03 marks)
6.(a) At 27◦C two moles of an ideal mono atomic gas occupy a volume V. The gas expands adiabatically to a volume 2V, calculate
(i)Change in its internal energy(02![]() marks)
marks)
(ii)The work done by the gas during the process(02![]() marks)
marks)
(b)(i) What is Wien’s displacement law? Give one limitation of this law.
(02 marks)
(ii)Two bodies A and B have thermal emissivity of 0.01 and 0.81 respectively. The outer surface areas of the two bodies are the same. The two bodies emit total radiant power at the same rate. The wavelength λB corresponding to maximum spectral radiancy from B is shifted from the wavelength corresponding to maximum spectral radiancy in the radiation from A by 1.0µm. If the temperature of A is 5802K, calculate the wavelength of B (λB )(03 marks)
7.(a) (i) The main interior of the earth core is believed to be in molten form. What is seismic evidence supports this believe? (03 marks)
(ii) Explain why the Ozone layers on the top of the stratosphere is crucial for human survival?(03 marks)
(b)(i) List down four physical changes that took place at a location just before onset of an earthquake at that particular location. (02 marks)
(ii)What are the advantages of windbreaks to plant environment? (02 marks)
SECTION B (30 marks)
Answer only two (2) questions in this section.
8.(a) (i) Briefly explain why a.c is most useful for domestic uses of electricity supply than d.c?(02 marks)
(ii) What is the advantage of using a greater length of a potentiometer wire? (02 marks)
(iii) Why is wheatstone bridge not suitable for measuring low resistance? (02 marks)
(b)(i) Define the term junction as applied in electrical network.(02 marks)
(ii)Find the current through each of the resistor in a circuit below. The batteries have negligible internal resistances. (03 marks)
(c)A coil having a resistance of 7Ω and inductance of 31.8µH is connected to a 230V, 50Hz supply. Calculate
(i)Circuit current(01 marks)
(ii)Phase angle(01 marks)
(iii)Power factor and power consumed(02 marks)
9.(a) (i) An operating amplifier has an open loop gain of 10000. Calculate the amplifier gain when 10% of the output is fed back to the inverting input.
(02 marks)
(ii) The figure shown below has a supply voltage of 15V. The input resistance is 1.6KΩ and the feedback resistance is 20kΩ. Calculate the output voltage when the input voltage is 1.8V(02 marks)
(b)(i) What do you understand by the term logic gate? (02 marks)
(ii) In the circuit shown in figure below, identify the equivalent gate of the circuit.(03 marks)
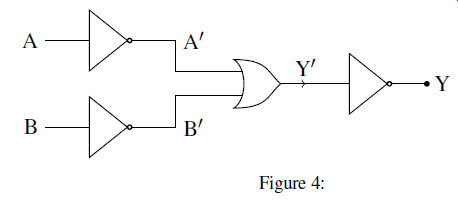
(c)(i) Why high frequency carrier wave are needed for effective transmission?
(02 marks)
(ii) A sinusoidal carrier voltage of frequency 1MHz and amplitude 100volts is amplitude modulated by sinusoidal voltage of frequency 5kHz producing 50% modulation. Calculate the frequency and amplitude of lower and upper side band terms.(04 marks)
10.(a) (i) Where doestheFermilevellieinaconductor,insulatorand semiconductor?(02 marks)
(ii)Why is a p-n junction also called junction diode?(02 marks)
(b)(i) Why does the width of depletion layer of p-n junction increase in reverse biasing? (02 marks)
(ii) A common emitter amplifier has an input resistance of 0.5kΩ and an output resistance of 45kΩ. If β = 65, Find the voltage gain and power gain.(03![]() marks)
marks)
(c) In the figure below, VBB supply can be varied from 0V to 5.0V. The Silicon transistor has βdc = 250 andRB = 100kΩ, RC = 1kΩ, VCC = 5.0V. Assume that when the transistor is saturated VCE = 0V and VBE = 0.8V.
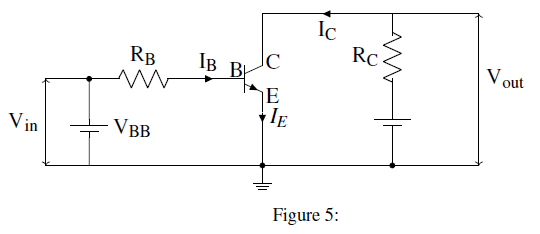
Calculate
(i) The minimum base current for which the transistor will reach saturation
(03 marks) (ii) Determine Vi when the transistor is switched on.(02![]() marks)
marks)
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 5
FORM SIX PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 5
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256







